Understanding Phishing and How to Protect Yourself

In today’s digital age, cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with phishing being one of the most common and dangerous online threats. We want to help you understand what phishing is, how it works, and how you can protect yourself.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of cyber-attack where criminals impersonate legitimate organizations, such as banks, government agencies, or well-known companies, to steal sensitive information like usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, and Social Security numbers. These attacks are typically carried out through fraudulent emails, text messages, phone calls, or fake websites designed to trick you into providing personal details.
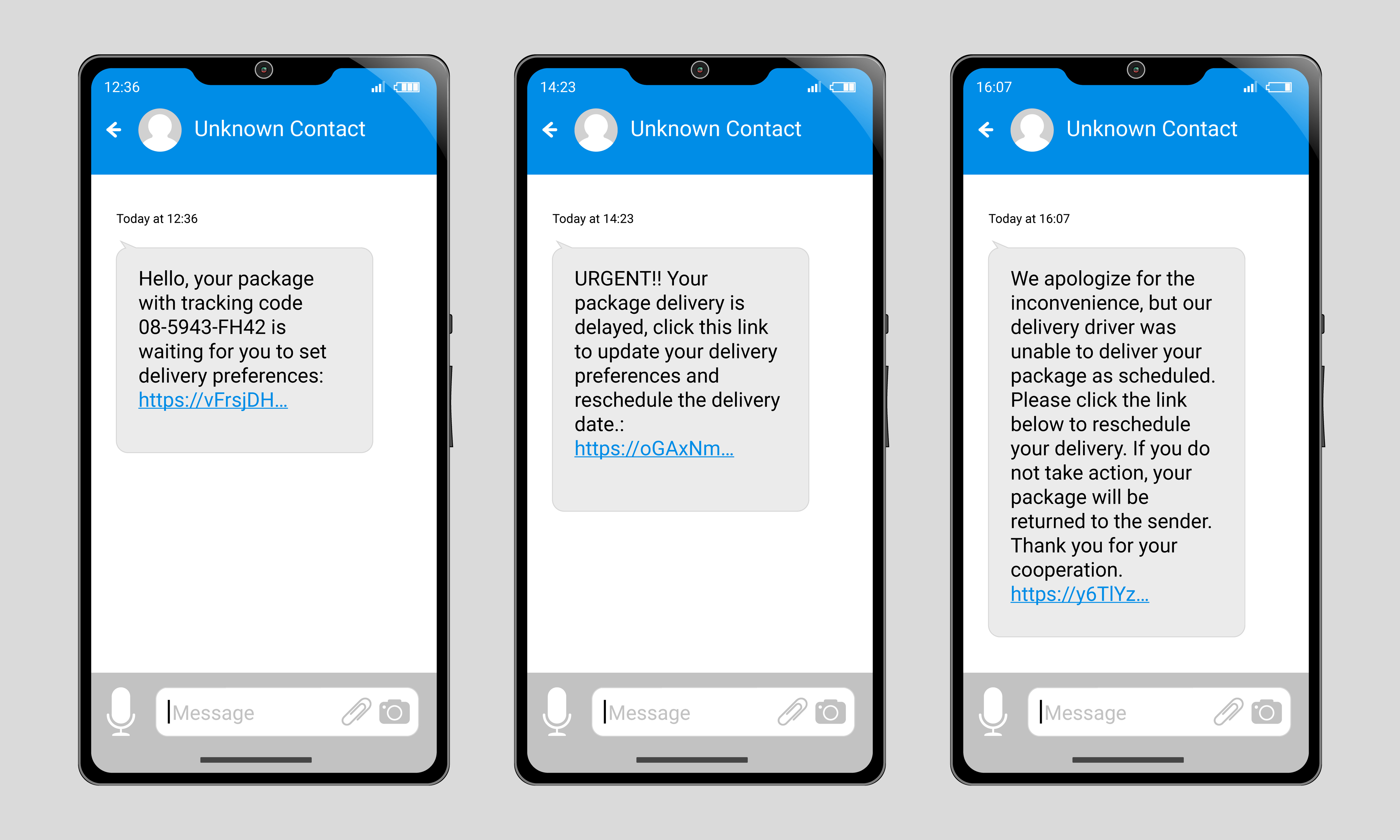
How Does Phishing Work?
Phishing attacks often rely on deception and urgency to lure victims. Here’s how they typically unfold:
- Fraudulent Communication: You might receive an email or text message that looks like it’s from a trusted source. It could claim there’s an issue with your account, a missed payment, failed delivery attempt, or a limited-time offer requiring immediate action.
- Call to Action: The message may include a link to a fake website or urge you to download an attachment. These links or downloads often lead to malicious software or websites designed to steal your information.
- Information Theft: If you follow the instructions, such as entering your credentials on a fake site or downloading malware, your sensitive information could be compromised.
How to Recognize Phishing Attempts
Phishing scams are becoming increasingly convincing, but there are still telltale signs to watch for:
- Generic Greetings: Messages starting with “Dear Customer” instead of addressing you by name.
- Misspellings and Poor Grammar: Legitimate organizations usually proofread their communications.
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Claims like “Your account will be locked” are designed to create panic.
- Suspicious Links: Hover over any links to see where they actually lead. Phishing links often mimic legitimate URLs but with slight alterations (e.g., www.stockrnanbank.com instead of www.stockmanbank.com).
- Unsolicited Attachments: Banks and reputable companies rarely send attachments unless expected.
How to Protect Yourself from Phishing
- Verify the Source: If you receive an unexpected message, contact the organization directly using official contact information, not the details provided in the suspicious message.
- Think Before You Click: Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or untrusted sources.
- Use Strong Security Measures: Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your accounts, regularly update your passwords, and use a unique password for each account.
- Install Security Software: Keep your antivirus software updated to detect and block phishing attempts.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Regularly review your bank statements and credit reports for any unauthorized transactions or changes.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest phishing scams and tactics.
What to Do If You Fall Victim to Phishing
- Change Your Passwords: Immediately update your login credentials for any compromised accounts.
- Contact Your Bank: Inform us so we can help secure your account and monitor for fraudulent activity.
- Report the Incident: Notify the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at ReportFraud.FTC.gov.
Your Security Is Our Priority
If you ever receive suspicious messages claiming to be from us, don’t hesitate to verify their authenticity by reaching out to us directly. By staying vigilant and informed, you can outsmart phishing attempts.
For more information about phishing, visit the FBI's Phishing and Spoofing page, or contact us.


